A Local Area Network (LAN) cable, commonly known as an Ethernet cable, is a type of cable used in computer networking to establish a wired connection between devices within a local area network. It is a fundamental component in creating a reliable and high-speed network infrastructure for various applications. In this article, we will explore what a LAN cable is, its primary purpose in computer networking, its different types, and its advantages over wireless alternatives.
What is a LAN Cable?
A LAN cable is a physical medium used to transmit data between devices within a limited geographical area, typically within a building, campus, or home. It is designed to provide a reliable and secure wired connection that allows devices to communicate with each other and access shared resources such as files, printers, and internet connectivity. LAN cables come in various categories and types, with each designed to support different data transmission speeds and network requirements.
Primary Purpose in Computer Networking:
The primary purpose of a LAN cable in computer networking is to facilitate data communication between devices within a local network. It establishes a physical connection that allows computers, servers, routers, switches, and other networked devices to exchange data packets seamlessly. Some of the key roles of LAN cables in computer networking include:
Data Transmission: LAN cables serve as a reliable and high-speed medium for transmitting data between devices. They enable fast and consistent data transfer rates, crucial for applications that require low latency, such as online gaming, video conferencing, and real-time data processing.
Interconnectivity: LAN cables connect various networked devices, forming the backbone of the local network infrastructure. This interconnectedness allows devices to share information and resources, fostering collaboration and productivity within the network environment.
Internet Connectivity: LAN cables are used to connect local network devices to a router or modem, providing access to the internet. This is especially important in businesses, homes, and institutions where multiple devices require internet connectivity.
File Sharing and Network Printing: Through the LAN cable, devices on the network can easily share files and resources, including printers and other peripherals. This promotes efficient collaboration and resource utilization.
Network Security: Wired LAN connections offer enhanced security compared to wireless connections. LAN cables are less susceptible to unauthorized access or interception, providing a more secure environment for sensitive data transmission.
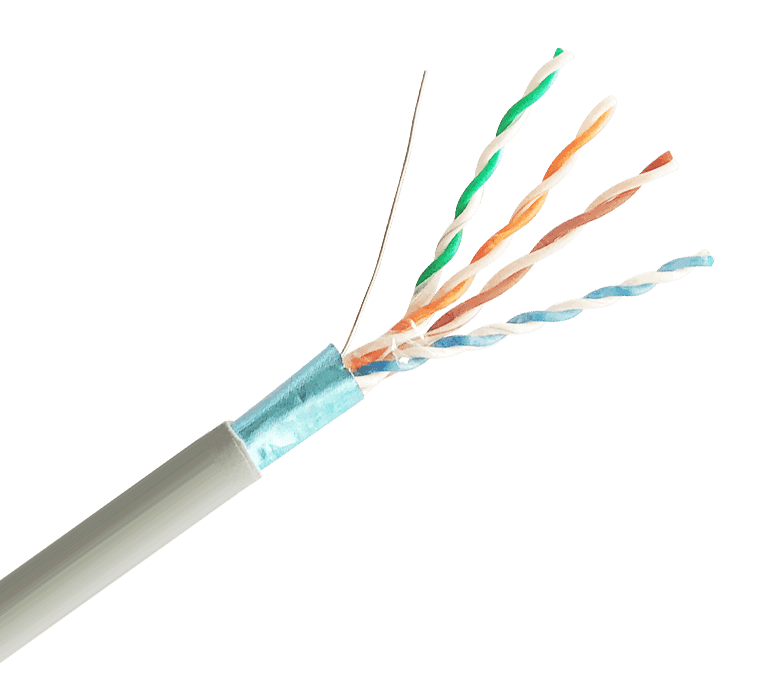
Types of LAN Cables:
There are several types of LAN cables, each designed to support different data transmission speeds and network requirements. The most common types of LAN cables are:
Category 5e (Cat 5e): Cat 5e cables are widely used for Fast Ethernet (10/100 Mbps) and Gigabit Ethernet (1000 Mbps) networks. They have four pairs of twisted copper wires and are capable of transmitting data at speeds up to 1000 Mbps over distances of up to 100 meters (328 feet).
Category 6 (Cat 6): Cat 6 cables provide improved performance over Cat 5e and are designed for Gigabit Ethernet and 10-Gigabit Ethernet (10,000 Mbps) networks. They offer better shielding and reduced crosstalk, enabling higher data transmission speeds and longer distances.
Category 6a (Cat 6a): Cat 6a cables are an enhanced version of Cat 6 cables, supporting even higher data transmission speeds up to 10 Gbps over longer distances. They are commonly used in data centers and enterprise networks.
Category 7 (Cat 7): Cat 7 cables offer further improvements in shielding and crosstalk reduction, making them suitable for 10-Gigabit Ethernet and higher-speed networks. They are backward compatible with lower-category cables and are often used in industrial environments.
Advantages over Wireless Alternatives:
While wireless networking has gained popularity, LAN cables continue to offer several advantages over wireless alternatives in specific scenarios:
Reliable Connection: LAN cables provide a stable and consistent connection with minimal interference or signal loss, ensuring reliable data transmission.
Lower Latency: Wired connections generally have lower latency compared to wireless, making them ideal for applications that require real-time data exchange, such as online gaming and video conferencing.
Enhanced Security: Wired LAN connections are more secure, as they are not as vulnerable to unauthorized access or interference from external devices.
Greater Bandwidth: LAN cables, especially the higher-category cables, offer greater bandwidth capacity, allowing for higher data transmission speeds and more efficient network performance.
Reduced Congestion: In environments with a high density of wireless devices, using LAN cables can help reduce wireless congestion and improve overall network performance.
In conclusion, a LAN cable is a physical medium used in computer networking to create a wired connection between devices within a local area network. Its primary purpose is to facilitate data communication, internet connectivity, file sharing, and resource access among networked devices. LAN cables come in various categories, each supporting different data transmission speeds, and they offer several advantages over wireless alternatives, such as reliability, lower latency, enhanced security, greater bandwidth, and reduced congestion. Whether in a business, home, or institutional setting, LAN cables play a vital role in establishing a robust and efficient network infrastructure for seamless data exchange and collaboration.





 浙公网安备33018502001191号
浙公网安备33018502001191号