Indoor optical cables achieve high-speed data transmission speeds through a combination of advanced technologies and optical properties. Here's how they achieve these speeds:
Light-Based Transmission: Unlike traditional copper cables that transmit data using electrical signals, optical fiber cables use light to transmit data. This light-based transmission is incredibly fast because light travels at near the speed of light in a vacuum, which is approximately 299,792,458 meters per second (about 186,282 miles per second). This inherent speed advantage contributes significantly to high-speed data transmission.
High Bandwidth: Optical fibers have a much higher bandwidth compared to copper cables. Bandwidth refers to the data-carrying capacity of the cable. The core of an optical fiber is extremely thin, typically around 9 micrometers (µm) for single-mode fiber, allowing it to carry a vast amount of data simultaneously. This high bandwidth enables the transmission of large amounts of data at high speeds.
Low Signal Attenuation: Optical fibers have very low signal attenuation, meaning that the light signals can travel long distances without significant loss of signal strength. This property allows data to be transmitted over long distances without the need for frequent signal amplification, which is often required for copper cables. Low attenuation is critical for maintaining high-speed data transmission over extended indoor cable runs.
Multimode and Single-Mode Fibers: Indoor optical cables can utilize both multimode and single-mode fibers. Multimode fibers are commonly used for short-distance, high-speed data transmission within buildings and data centers. Single-mode fibers, on the other hand, are used for long-distance, high-speed data transmission over larger indoor areas or between buildings.
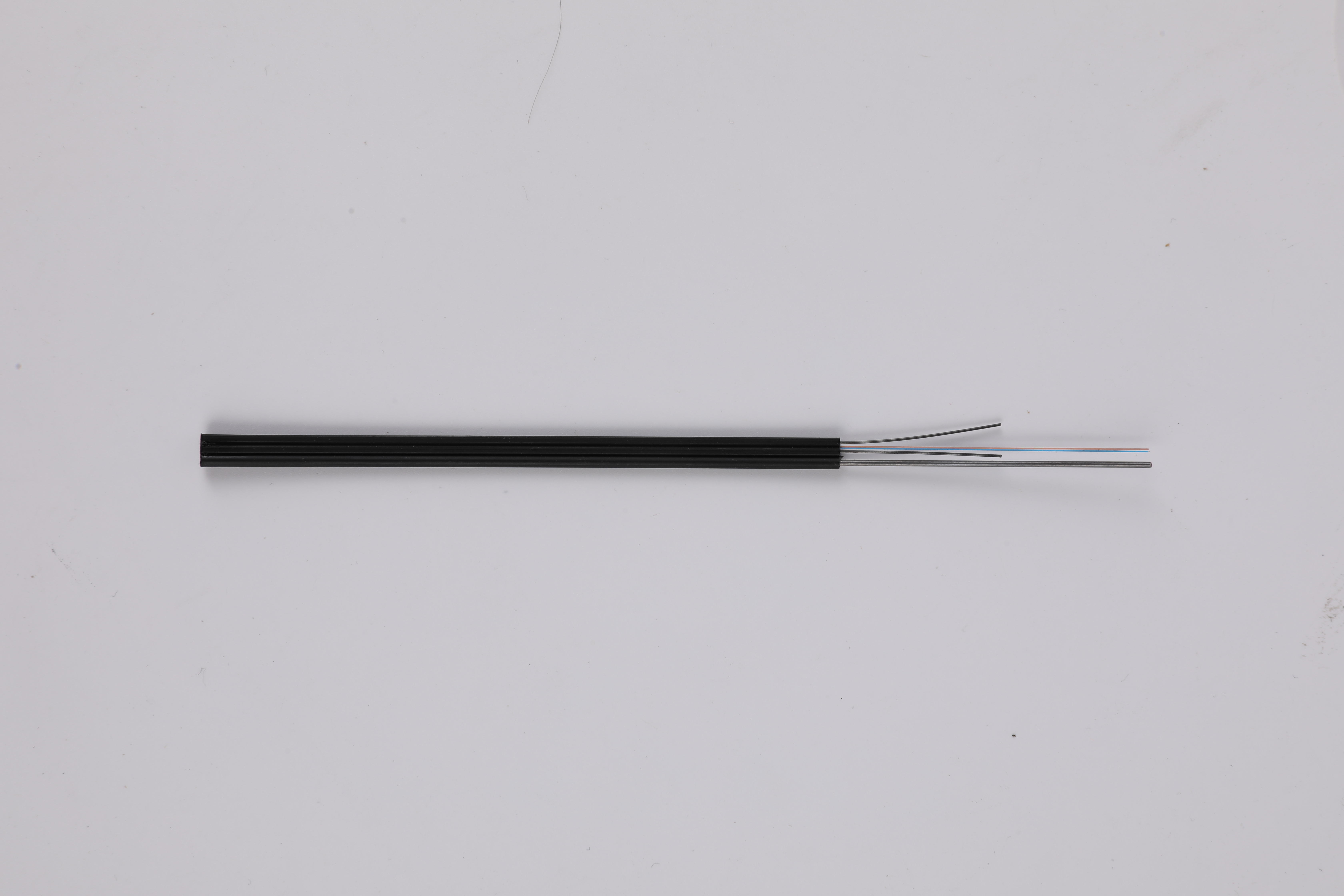

Advanced Modulation Techniques: Advanced modulation techniques, such as phase modulation and amplitude modulation, are used to encode data onto the light signals. These techniques allow for the transmission of multiple bits of data per light pulse, further increasing the data transmission speed.
Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM): WDM is a technology that allows multiple wavelengths (colors) of light to be transmitted over a single optical fiber. Each wavelength can carry a separate data stream. By using WDM, indoor optical cables can achieve even higher data transmission speeds by multiplexing multiple data channels over a single fiber.
Low Latency: Optical fiber cables offer low latency, meaning that data travels through the cable with minimal delay. Low latency is essential for high-speed data transmission applications, such as online gaming, real-time video conferencing, and financial transactions.
In summary, indoor optical cables achieve high-speed data transmission by harnessing the speed of light, offering high bandwidth, minimizing signal loss, and employing advanced technologies like modulation and multiplexing. These characteristics make them the preferred choice for high-speed data transmission in indoor environments, supporting applications ranging from internet connectivity to data center networking.





 浙公网安备33018502001191号
浙公网安备33018502001191号